The endoplasmic reticulum or ER is an organelle that takes up ten percent of the cell. There are two kinds of endoplasmic reticulum: smooth endoplasmic reticulum or SER and rough endoplasmic reticulum or RER.

Components of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER is made of flattened sacs and branching tubules that are connected by a single membrane to make a complex lumen(internal space).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is called rough because it is covered with ribosomes. 
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is called smooth because it is not covered with ribosomes.
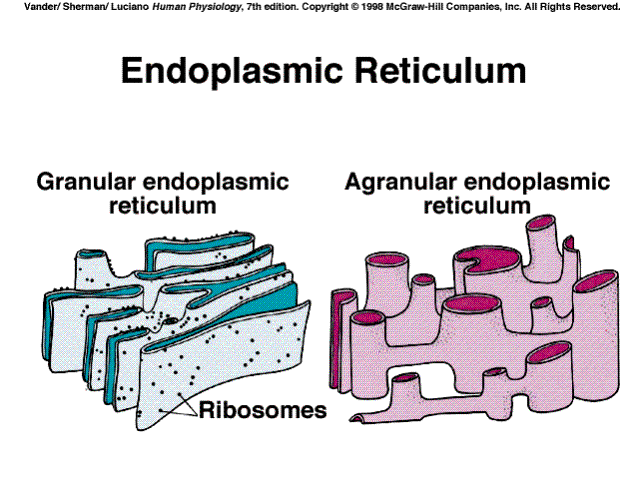
Specific Functions of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER transports proteins within the cell. It is like the cell's highway.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The RER is involved with the production and exportation of proteins, glycoproteins, and hormones.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The SER produces lipids and steroids. It has enzymes that breakdown toxins.
How the Specific Functions of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Occur
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The RER produces protein using ribosomes which make amino acids into protein units.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The SER’s smooth surface allows it to hold enzymes which are used to break down toxins.
Role of the ER from a Physiological Standpoint
The ER enables the muscles of the body to contract when it releases calcium ions. When the enzymes break down toxins, it is easier to flush out the body of harmful things.
Types of Cells in which ER is Present
The ER is in both plant and animal cells.


Other Facts
· Endo refers to within the cytoplasm.
· Reticulum means network.
Works Cited
- n.d. Endoplasmic Reticulum. Retrieved September 21, 2008, from http://cellstructure.pbwiki.com/Endoplasmic-Reticulum_3rd#pbedit
- Davidson, Michael. 2008. The Endoplasmic Reticulum. Retrieved September 21, 2008, from http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html
- 2008. The Endoplasmic Reticulum. Retrieved Semptember 21, 2008, from http://www.cliffsnotes.com/WileyCDA/Section/What-does-the-endoplasmic-reticulum-ER-do-.id-305406,articleId-7883.html
- 2008. The Endoplasmic Reticulum. Retrieved Semptember 21, 2008, from http://www.bscb.org/?url=softcell/er
FAQ
1. What are ribosomes? Ribosomes are an organelle that synthesize proteins in the cell.
2. How does the ER affect humans? It flushes out harmful things in the body.
3. What is round inside of the ER? The nuclear envelope is the round thing inside the ER.
4. How does this affect the human body? It flushes out harmful things in the body.
5. What sort of enzymes break down the protein in the SER? The enzymes in the SER do not break down protein, they break down toxins.
6. Why do we need both the rough and smooth ER? Because the rough ER produces proteins, and the smooth ER gets rid of harmful toxins in the body.
7. Are the functions different in plant and animal cells? The functions of the ER is the same in plant and animal cells because all organisms need proteins.
8. What makes up the other 90% of the cell? The other organelles and the cytoplasm.
9. Why are there two different kinds of ER? There are two different kinds of ER because one has ribosomes(RER) and the other does not(SER).
10. Is there a difference from the plant cell ER and animal cell ER? There is not really a big difference.
11. Are the RER or the SER found in eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells? The RER and the SER are found only in eukaryotic cells.
12. What do the ribosomes on the ER do. Ribosomes make amino acids into protein units.
13. How quickly can the rough ER produce proteins? There is no limit to how long it takes the RER to produce proteins.
14. What is the cisternal space? The cisternal space is the lumen or the internal space of the ER.
Comments (17)
Katie G said
at 10:02 am on Sep 18, 2008
what are ribosomes?
Kerri Loftis said
at 10:02 am on Sep 18, 2008
How does the ER effect humans?
Shelby Williams said
at 10:04 am on Sep 18, 2008
What is round inside of the ER?
- said
at 10:05 am on Sep 18, 2008
How does this effect the human body?
Benjamin Miller said
at 10:08 am on Sep 18, 2008
What sort of enzymes break down the protein in the SER?
Louisa said
at 10:18 am on Sep 18, 2008
why do we need both the rough and smoothe ER?
Margarita said
at 10:20 am on Sep 18, 2008
Are the functions different in animal and plant cells?
(Again, to make the layout look more even, try centering pictures and text. The eye will travel up and down rather than all over the page to look for the next segment of information. Otherwise, great job! ^__^)
jordan hansen said
at 10:23 am on Sep 18, 2008
what makes uo the other 90% of the cell?
lieren bodiford said
at 10:36 am on Sep 18, 2008
why are there 2 different kinds of er's?
lexi said
at 6:57 pm on Sep 18, 2008
how does the ER synthesize lipids and protiens?
Kayla Joslin said
at 10:02 pm on Sep 18, 2008
Are the RER or the SER found in eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells?
savanna brown said
at 10:28 pm on Sep 18, 2008
what do the ribosomes on the ER do?
Mary Emily Fox said
at 9:54 am on Sep 19, 2008
How quickly can the rough ER produce proteins?
avonalmen said
at 10:15 am on Sep 19, 2008
Does the ER play a different role in the plant and animal cell or does function as the same in each?
lexi said
at 10:17 am on Sep 19, 2008
is there a differnce from the a plant cell ER and an animal cell ER?
Leandro N. said
at 10:22 am on Sep 19, 2008
what is the cisternal space?
Samantha Zebra said
at 10:36 am on Sep 19, 2008
are the plant and animal ER different?
You don't have permission to comment on this page.